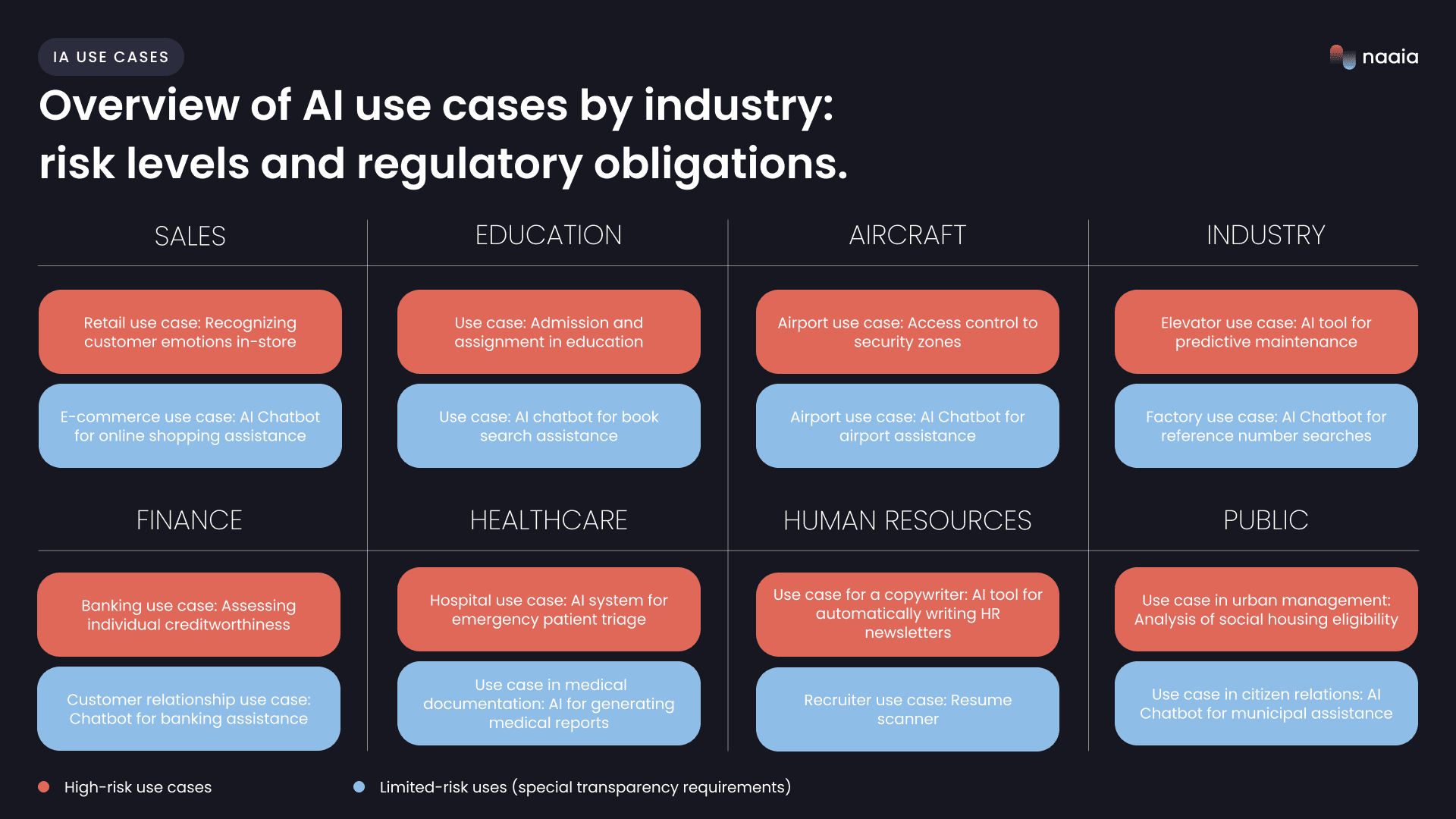
AI usage is profoundly transforming industries and ways of working. From the automation of tasks to the optimization of complex processes, AI opens up a huge range of possibilities. But not all these uses present the same level of risk: some have a direct impact on security, fundamental rights or privacy, requiring strict supervision, while others impose transparency obligations or can be adopted without any particular constraints. To ensure responsible adoption, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles of responsible AI and to master the associated issues.
To ensure responsible adoption, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles of responsible AI and to master the associated issues. Some uses are classified as high risk because they directly affect security, fundamental rights or privacy. Others, although less sensitive, impose transparency obligations to ensure ethical use. Finally, some applications are considered to be of minimal risk, requiring neither a strict regulatory framework nor enhanced governance measures.
In this article, we explore the main use cases of AI across different industries, detailing the associated risk levels and regulatory requirements to be taken into account.
AI in human resources: Recruitment and talent management
1. High-risk use case
A – Use case for a recruiter: CV scanner
Companies are increasingly using AI tools to automatically analyze applications. These systems extract key information such as skills and professional experience, in order to speed up the selection of profiles. However, these algorithms can introduce discriminatory biases, excluding certain candidates on irrelevant criteria.
B – Business use case: Performance monitoring and optimization
Some companies deploy AI systems capable of analyzing employee productivity in real time. These tools monitor task completion, team interactions and performance evaluations. While they optimize the organization of work, they raise ethical questions about workplace surveillance and the protection of personal data.
2. Low-risk use cases (special transparency requirements)
Use case for a writer: AI tool for automatic drafting of HR newsletters
HR departments use AI tools to generate internal newsletters, summarizing important announcements, company events and managerial communications. Although these tools do not have a critical impact, employees should be made aware that the communications are generated by AI.
AI in finance: Credit, insurance and customer relations
1. High-risk use cases
A – Use cases in banking: Assessment of individual creditworthiness
Banks use AI to analyze financial and behavioral data to calculate a credit score. To ensure compliant and controlled use, it is recommended to follow an AI framework to ensure compliance and risk management. This system speeds up loan approval decisions, but poses a risk in the event of algorithmic bias, which can lead to the unjustified exclusion of certain profiles.
B – Use case in insurance: Risk assessment and pricing
The AI examines medical, demographic and behavioral criteria to adjust insurance premiums. While this approach improves the personalization of offers, it raises equity issues and can make certain financial services inaccessible to vulnerable populations.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency obligations)
Customer-related use case: banking assistance chatbot
Banks are integrating AI chatbots to help their customers carry out day-to-day operations such as checking their accounts and making transfers. These assistants must clearly inform users that they are interacting with an AI.
AI in the public sector: automation of administrative decisions
1. High-risk use case
A – Use case in urban management: Analysis of eligibility for social housing
Local authorities use algorithms to process applications for social housing based on applicants’ socio-economic criteria. Poor calibration of the model can lead to unfair decisions and increase inequalities in access to housing.
B – Use case in immigration: Automated decision for granting residence permits
Public administrations are adopting AI to improve services, but must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure ethical and compliant implementation. Migration administrations rely on AI to review applications for residence permits. These systems must be regulated to avoid any blind automation of sensitive decisions and to guarantee human intervention.
C – Use case: Intelligent traffic light management in a city
A city deploys an AI system as a safety component for its traffic management. The system analyzes the flow of vehicles in real time using sensors and cameras installed at intersections. It automatically adjusts the timing of traffic lights to optimize traffic flow, reduce traffic jams and minimize energy consumption, while guaranteeing maximum safety for road users.
D – Use case for water: AI system for water management in the city
A local authority is deploying an AI system to optimize water management. This system analyzes data from distribution networks and quality sensors in real time, detects leaks and anticipates consumption peaks. It thus enables the efficient planning of supply, the reduction of losses and the optimal distribution of water in the city.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency obligations)
A – Use case in citizen relations: AI chatbot for municipal assistance
Many town halls are deploying chatbots to answer citizens’ administrative questions. These tools facilitate access to information, provided that users are aware that they are interacting with an automated system.
B – Use case: AI tool for public health information
This AI tool provides up-to-date information on public health, including vaccination programs, epidemic prevention and other topics of public interest. By aggregating data from official sources and health organizations, it enables citizens and professionals to quickly obtain accurate and reliable answers on current health measures and health recommendations.
AI in the Police and Justice: Drafting, evaluation and assistance
1. High-risk use cases
A – Police use case: Victimization risk assessment
Law enforcement authorities use an AI system to analyze sociodemographic, geographic and behavioral data to identify individuals or areas at increased risk of becoming victims of criminal offenses. This tool helps to guide preventive actions and strengthen the protection of vulnerable individuals.
B – Court use case: AI assistance in drafting court decisions
A court implements an AI solution to assist magistrates in preparing judgments. The system analyzes legal documents, precedents and relevant legislation to generate structured summaries and recommendations.
C – Court use case: AI tool to aid interpretation and application of the law
A court uses an AI system to facilitate the research and interpretation of facts as well as the application of the law in the context of a dispute. This tool makes it possible to quickly identify probative elements, analyze relevant precedents and formulate recommendations for a more precise and equitable application of the legislation, thus helping to speed up the decision-making process, including in out-of-court settlements.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency obligations)
Police use case: chatbot support
An AI chatbot is deployed by the police to provide citizens with practical information. It provides quick access to information on how to file a complaint, police station numbers and good safety practices, thus facilitating communication between the police and the public.
AI in education: Admission, learning and exam supervision
1. High-risk use case
A – Use case: Admission and placement in education
An educational institution uses an AI system to process and analyze all application files. This system examines transcripts, standardized test scores, and other academic and extracurricular criteria to determine not only the admission of candidates, but also their placement in different programs or levels of training. By cross-referencing this data, the system proposes a distribution of students in the courses that best correspond to their skills and profiles.
B – Use case: Monitoring and detection of prohibited behavior during exams
During exam sessions, a training establishment deploys an AI system capable of analyzing in real time the video streams captured in the room. The system automatically identifies suspicious behavior, such as the unauthorized use of electronic devices or inappropriate exchanges between candidates, by detecting abnormal movements or postures.
2. Use cases with limited risk (Special transparency obligations)
A – Use case: AI chatbot to assist in the search for books
A university library uses an AI chatbot to help users locate books in its catalog. The system allows users to search for books by querying the database using criteria such as title, author or subject, thus offering immediate assistance in finding the desired books without providing personalized recommendations.
B – Use case: AI tool for summarizing news articles
A school provides an artificial intelligence system that automatically summarizes news articles. This service gives students quick access to the essential points of the news, making it easier to understand and critically analyze media content without requiring an exhaustive reading of each article.
AI in healthcare: diagnosis, triage and medical assistance
1. High-risk use cases
A – Hospital use case: AI system for emergency patient triage
Emergency departments use algorithms to classify patients according to the severity of their condition. Although these systems improve the responsiveness of care, misclassification can delay the management of critical cases.
B – Medical diagnostic use case: AI medical device for diagnostic assistance
Hospitals are integrating AI tools to analyze medical imaging and detect anomalies. These systems must be medically validated to avoid diagnostic errors.
C – Robot-assisted surgery with AI integration
A hospital is implementing a robot-assisted surgery system that integrates artificial intelligence to optimize the precision and safety of interventions. The AI module first analyzes the patient’s medical images to develop a personalized surgical plan, taking into account the specific anatomy. During the operation, the AI processes sensor and image data in real time, dynamically adjusting the robot’s movements to improve the accuracy of incisions and sutures, reduce tissue trauma and promote faster recovery.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency obligations)
Use cases in medical documentation: AI-based tool for generating medical reports
AI solutions synthesize exchanges between doctors and patients to automatically generate detailed medical reports. Professionals must be informed of the automated nature of the summary in order to validate it.
AI in aviation: Security, access control and passenger assistance
1. High-risk use case
A – Airport use case: Access control to security areas
An airport deploys an AI biometric recognition system to identify in real time who is in restricted areas, such as airside and security restricted areas. This system captures the biometric data of those present and compares it to a pre-registered database, thus identifying authorized profiles and quickly identifying intruders or unregistered persons.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency obligations)
A – Airport use case: AI chatbot for airport assistance
An airline is deploying an AI-based chatbot to provide agents with instant answers to customer questions in different languages. The tool queries the company’s internal reference systems and procedures to generate precise answers concerning, for example, the check-in process, access to waiting rooms or boarding procedures.
B – Use case of an airline: Biometric verification to confirm passenger identity
An airline is implementing a biometric AI system whose sole purpose is to confirm that a specific individual is who they claim to be. During boarding, the device captures the passenger’s biometric data and compares it with the recorded data, thus ensuring that the individual matches the information provided, without going beyond this verification function.
AI in commerce and mass distribution: Customer experience and security
1. High-risk use cases
A – Retail use case: Recognition of customer emotions in-store
Some retailers use cameras coupled with AI to analyze customer reactions and adapt their marketing strategy. These technologies require strict supervision to guarantee respect for privacy.
B – Retail use case: AI-based retroactive identification of shoplifters
A store is deploying an AI system that analyzes CCTV footage to retroactively identify people suspected of shoplifting. This system compares the physical characteristics of the individuals spotted with existing databases to facilitate investigations and support enforcement actions.
C – Retail use case: Recognition of emotions during a marketing event
During a product launch event, an AI system is deployed to analyze customers’ emotional reactions in real time. Using cameras and sensors, the tool detects facial expressions and other emotional indicators to measure the enthusiasm, interest or reservations of the participants. This information enables marketing teams to adapt their communication and optimize the impact of the event.
2. Use cases with limited risk (specific transparency requirements)
A – E-commerce use case: AI chatbot for online shopping assistance
Online sales sites deploy AI assistants to advise consumers on their shopping journey. It is essential to ensure that these chatbots remain neutral and do not influence decisions in a misleading way.
B – Marketing use case: AI tool for creating fictional images for commercial purposes
A marketing company adopts a generative AI tool capable of creating personalized fictitious images for its advertising campaigns and visual media. This tool makes it possible to quickly produce innovative visuals, including the possibility of generating deep fakes, in order to simulate scenarios or present products in an impactful way.
AI in industry and innovation: Maintenance, production and safety
1. High-risk use case
A – Elevator use case: AI tool for predictive maintenance
An elevator is equipped with an AI tool that continuously monitors its mechanical and electrical parameters. The AI analyzes data in real time, the system anticipates potential failures and triggers alerts for preventive intervention, thus optimizing the safety and availability of the elevator while reducing maintenance costs.
B – Predictive maintenance use case: Intelligent gas fireplace with AI combustion control
An intelligent gas fireplace incorporates an AI-based control system that monitors and adjusts its combustion process in real time. By continuously analyzing data from sensors (temperature, flame intensity, gas flow), this system optimizes fuel consumption, reduces polluting emissions and quickly detects any anomalies, thus ensuring optimal performance and predictive maintenance.
C – Use case in a factory: Intelligent mask integrating AI in a factory
In a factory where harmful particles and gases are likely to affect workers’ health, an intelligent mask integrates sensors and AI to continuously monitor air quality and respiratory parameters. When the mask detects a high concentration of pollutants or a malfunction in breathing, it automatically adjusts its level of filtration and issues an immediate alert via a visual or audible signal.
D – Nuclear use case: Employee identification system and verification that protective equipment is being worn in a nuclear power plant
In a nuclear power plant, an AI system combines biometric recognition and image analysis to identify employees and verify that they are wearing their hard hats and other mandatory protective equipment. The system monitors sensitive areas in real time and, in the event of non-compliance with safety instructions, immediately alerts those responsible for rapid intervention.
E – Educational use case: Interactive toy integrating AI
An interactive toy integrates artificial intelligence to offer a fun and educational experience for children. For example, a companion robot recognizes the child’s voice and emotions, adapting its responses and activities according to the interactions. This toy offers games, tells stories and provides personalized feedback, stimulating the child’s learning and imagination. It is designed not to use any subliminal, manipulative or deceptive techniques, and does not take advantage of any vulnerability, thus guaranteeing ethical and safe use for the youngest children.
F – Automotive use case: semi-autonomous vehicle integrating AI
An automotive manufacturer is deploying a semi-autonomous driving system that integrates artificial intelligence to improve driving safety and comfort. The vehicle uses sensors, cameras and machine learning algorithms to analyze its environment in real time, detect obstacles and adjust its trajectory according to traffic conditions. In semi-autonomous mode, the system takes care of tasks such as lane keeping, speed adaptation and safe distance management, while leaving final control to the driver.
G – Automotive use case: AI system for passenger safety in vehicles
In a modern vehicle, an AI system monitors sensor data in real time to detect driver fatigue or the presence of obstacles. In case of risk, it triggers alerts or activates assistance functions, thus enhancing occupant safety. In addition, the system can automatically adjust speed and trajectory to prevent accidents.
H – Factory use case: Remote biometric identification system for monitoring operators in an assembly plant
In an automobile assembly plant, a remote biometric identification system is set up to determine precisely who is involved in each stage of vehicle manufacturing. This system captures the biometric characteristics of employees when they arrive at a workstation and records their presence, thus ensuring complete and secure traceability of operations.
2. Limited Risk (Specific Transparency Requirements)
A -Factory use case: AI chatbot for searching for reference numbers
In a washing machine manufacturing plant, an AI-based chatbot helps employees quickly find product reference numbers. The tool queries technical databases and internal documentation to instantly provide the exact reference of a part or component, thus facilitating production management and equipment maintenance.
B – Business use case: Internal chatbot for document search and synthesis
An internal chatbot helps consultants easily find relevant documents in the company database. In addition to locating documents, it generates concise summaries and highlights key points, facilitating decision-making and rapid information sharing.
3. Minimal Risk
A – Operations use case: AI-based spam filter
An email system uses AI to automatically analyze and classify emails, identifying those considered unwanted.
B – Gaming use case: Video game with AI
A video game incorporates AI to animate non-player characters and adjust the difficulty based on the player’s behavior, creating a more responsive gaming experience.
C – Photography use case: AI tool for automatic photo brightness adjustment
An AI system is integrated into an image processing application to automatically analyze and correct the brightness of photos. Based on machine learning algorithms, the tool detects underexposed or overexposed areas and adjusts the lighting parameters to improve image quality.
D – Video use case: AI tool for video manipulation for professional editing purposes
An AI system is integrated into a post-production application to automatically analyze and optimize video footage. Using advanced algorithms, the tool facilitates editing by detecting key scenes, adjusting transitions and improving visual quality, thus saving time and increasing accuracy for film and television professionals.
Artificial intelligence is a powerful lever for improving our processes and optimizing our decisions. However, its integration must be supervised according to the risks it presents. High-risk applications require strict safeguards, those with limited risk impose transparency obligations, while uses with no significant impact can be adopted without regulatory constraints.
If we want to take full advantage of AI while ensuring responsible use, we must anticipate these issues and put appropriate safeguards in place.
Want to deepen your understanding of AI regulations and best practices? Check out our guide to governance frameworks to ensure compliance and risk management in your use cases.